Overview
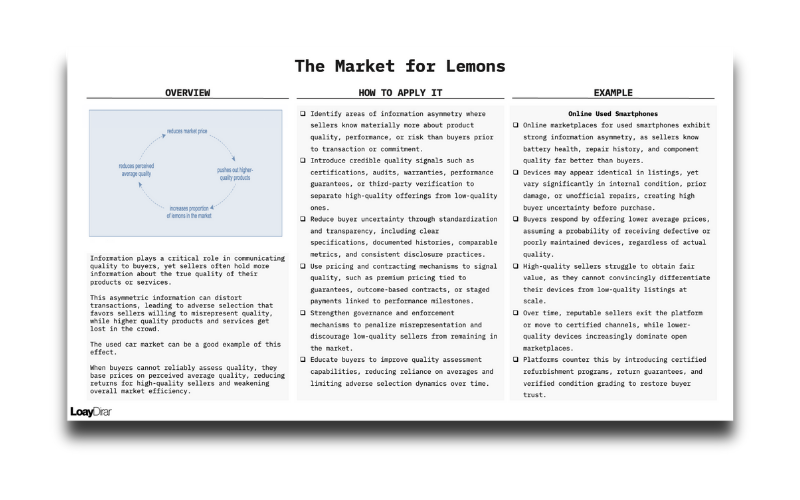
The Market for Lemons concept explains how information asymmetry between sellers and buyers can distort markets and lead to adverse selection. When sellers know more about product or service quality than buyers, low-quality offerings can thrive, while high-quality ones struggle to differentiate. As buyer uncertainty increases, average prices fall, discouraging reputable sellers and allowing inferior products (“lemons”) to dominate. Over time, this dynamic erodes trust, reduces overall market efficiency, and penalizes quality-driven participants.
How to Use It
Apply the concept by identifying where information asymmetry exists, assessing how buyers evaluate quality, and understanding pricing behavior driven by perceived average quality. Introduce credible signals such as certifications, guarantees, audits, warranties, or third-party verification to distinguish high-quality offerings. Strengthen transparency, disclosure, and enforcement mechanisms to reduce misrepresentation and rebalance the market.
Online Used Electronics Markets Example
In online marketplaces for used smartphones and electronics, sellers often possess superior knowledge of device condition, repair history, and performance. Without reliable quality signals, buyers discount prices to hedge against receiving defective products. Certified refurbishment programs, return guarantees, and verified condition grading have emerged as mechanisms to counter adverse selection and restore buyer confidence.